Influence of molecular design on the field-effect transistor characteristics of terthiophene polymers
McCulloch, I; Bailey, C; Giles, M; Heeney, M; Love, I; Shkunov, M; Sparrowe, D; Tierney, S
CHEMISTRY OF MATERIALS
2005
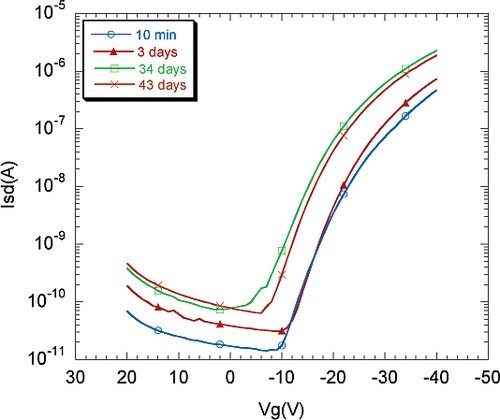
Polymers containing thiophene backbones have demonstrated the highest p-type field-effect mobility of any solution-processed polymer to date. One drawback of this class of polymers, however, is that they can possess a relatively low ionization potential, which, in the presence of oxygen, often results in spontaneous p-type doping. As a result, the transistor properties can change with time, leading to low current modulation caused by high off currents. In this work, we have explored strategies to chemically modify the thiophene backbone structure, which leads to changes in both the backbone conformation and microstructure as well as the electronic energy levels of the molecular orbitals. A series of terthiophene polymers were synthesized, and their physical and electrical properties reported. The effects of changes in molecular structure on transistor performance and air stability are discussed.